 |
||||||||||||||||


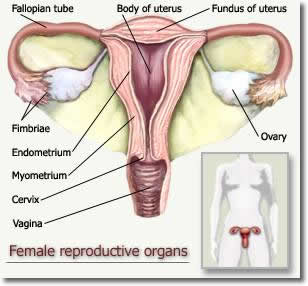
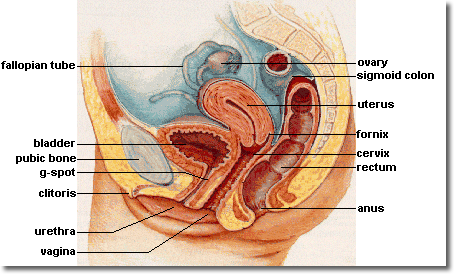
Glossary ACTIVE MANAGEMENT OF THIRD STAGE – is when a drug such as syntometrine is given to the woman as the baby is being born. It enables the uterus to contract and shear the placenta away from the uterine wall. The midwife delivers the placenta using the umbilical cord while the woman lies still. ALBA – the name for the colour of vaginal discharge after childbirth as it’s beginning to come to an end. It means white in colour. BRAXTON HICKS – are practice contractions. These contractions are thought to be the uterus getting ready for childbirth CERVIX - The cervix (from Latin "neck") is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes into the vagina. It can be visualised during procedures such as ‘smear tests’.
COLOSTRUM – is the first milk that the breast produces. It is thick and yellowish and has high concentrations of nutrients and immunities, but it is small in quantity. CONTRACTIONS – Under the influence of Oxytocin, the muscles of the uterus contract and release to dilate the cervix to aid delivery. CTG – Cardiotocograph, a machine that records a babys heart rate and frequency of contractions. DIAGNOSTIC TEST – A test that will diagnose for certain the abnormality it is testing for. An example being the Amniocentesis and diagnosis of Downs Syndrome. EFFACEMENT – is the term given to the process of the cervix shortening and becoming thinner until it lies flat and paper thin to the babys head, EMBRYO – Name given to the developing baby until eight weeks gestation. It is during this time that all the major organs are being formed. FETUS – Name given to a baby from eight weeks gestation until birth. It is during this time that the baby grows and matures until it is ready to cope in the outside world. FORCEPS DELIVERY – the use of a surgical forceps to aid delivery of an infant.
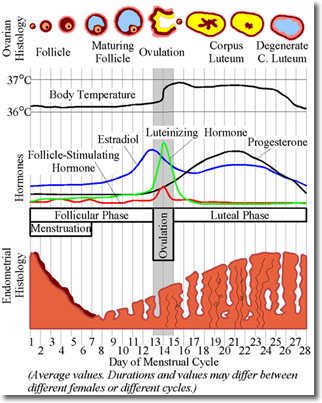
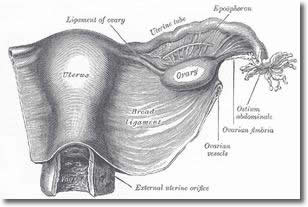
FUNDUS - The fundus of the uterus is the top portion opposite from the cervix. Fundal height, measured from the top of the pubic bone, is routinely measured in pregnancy to determine growth rates. HORMONE – is a substance secreted by certain glands which stimulates certain organs in the body. HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM - unrelenting, excessive pregnancy-related nausea and/or vomiting that prevents adequate intake of food and fluids. INHERITED – the transfer of characteristics from parent to child through genes. INVOLUTION – The name given to the process of a uterus returning to its pre pregnant state following childbirth. LABOUR – The name given to process of your cervix beginning to dilate to the baby being born. LETHARGY – tiredness that makes it difficult to get on with your normal daily activities. LIGAMENT - Fibrous tissue that connects bones (or two different parts of a single bone). LOCHIA - lochia is post-natal vaginal discharge, containingblood, mucus, and placental tissue. Lochia discharge typically continues for 4 to 6 weeks after childbirth. LUTEAL PHASE - From the beginning of a woman’s cycle, Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) influences a follicle in the ovary (where a single egg is stored) to mature. It is during the Luteal Phase that Luteinising Hormone surges and stimulates this follicle to swell and eventually rupture, releasing an egg. This is ovulation. Once ovulation has occurred the follicle is known as a Corpus Luteum. During the Luteal Phase, the Corpus Luteum produces Progesterone and this hormone is responsible for thickening the lining of the uterus, giving a fertilised egg a suitable environment to attach to.
Diagram source Wikipedia
MINOR DISORDERS – Name given to problems in pregnancy such as nausea that are irritating, but not dangerous.
OVULATION CYCLE -The Ovulation or Menstrual Cycle has four components. These being Menstruation, the Follicular Phase, Ovulation and the Luteal Phase. During the Follicular Phase a follicle in the ovary is stimulated by Follicle Stimulating Hormone to
Diagram source Wikipedia mature its egg. At the very end of this phase, Luteinising Hormone surges and under its influence the follicle erupts and the egg is released into the fallopian tube. This is ovulation. Following ovulation, the follicle is known as the Corpus Luteum and now the Luteal Phase begins. During this phase the Corpus Luteum produces Progesterone and this prepares the lining of the uterus for a fertilised egg. If the egg is not fertilised then the thick, spongy lining comes away and this is known as Menstruation or having your period. OXYTOCIN - is a hormone that also acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. In women, it is released mainly after distention of the cervix and vagina during labour, and after stimulation of the nipples, facilitating birth and breastfeeding, respectively. Oxytocin is released during orgasm in both sexes. In the brain, oxytocin is involved in social recognition and bonding, and might be involved in the formation of trust between people. PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES – exercises given to tighten the pelvic floor. Do this by tightening the muscles around your urethra, vagina and anus, as if trying to stop passing urine or opening your bowels. PERINEUM – The name given to the area between the vagina and anus. It contains muscle and fibrous tissue.
PHENYLALANINE – an essential amino acid PHYSIOLOGICAL THIRD STAGE – when the placenta is delivered by maternal effort and not aided by the use of syntometrine. PLACENTA - The placenta is composed of two parts, one of which is genetically and biologically part of the fetus, the other part of the mother. It is implanted in the wall of the uterus, where it receives nutrients and oxygen from the mother's blood and passes out waste. This interface forms a barrier, the placental barrier, which filters out some substances which could harm the fetus. However, many other substances are not filtered out, including alcohol and some chemicals associated with smoking cigarettes. Several types of viruses, such as Human Cytomegalovirus, may also cross this barrier; this often leads in various degrees of birth defects in the infant
In addition to the transfer of gases and nutrients, the placenta also has metabolic and endocrine activity. It produces, amongst other hormones, progesterone , which is important in maintaining the pregnancy; placental lactogen, which acts to increase the amount of glucose and lipids in the maternal blood; oestrogen; and human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG). This results in increased transfer of these nutrients to the fetus and is also the main cause of the increased blood sugar levels seen in pregnancy. POSTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND – is located at the base of the brain. It releases Oxytocin which is the hormone needed for labour and breastfeeding. RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES – when the membranes (bag) that surrounds the baby breaks. Women may notice a gush of fluid from the vagina when this happens. SCREENING TEST – A test that puts a person into a risk category of having a medical problem. An example would be the Barts blood test which puts a woman into a high or low risk group of having a baby with Downs Syndrome. SHOW – or the Operculum. This is the plug of mucous that fills the cervix during pregnancy. It protects the fetus from any infections that could reach it from the outside world via the vagina. STRESS INCONTINENCE - Stress incontinence is essentially due to pelvic floor muscle weakness. It is the loss of small amounts of urine with coughing, laughing, sneezing, exercising or other movements that increase intrabdominal pressure and thus increase pressure on the bladder. Physical changes resulting from pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause often cause stress incontinence. SUTURE – the name given to the material used by midwives and doctors in the process of repairing tears to the skin or other tissue. SYNTOMETRINE – is a drug given to women as the baby is born to aid delivery of the placenta and control blood loss. TENS – Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation. A form of pain relief. THYROXINE – hormone produced by the thyroid gland. One role of this hormone is to regulate tissue growth. UMBILICAL CORD - The umbilical cord is a tube that connects a developing embryo or fetus to its placenta. It contains three major vessels, buried within it for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen rich blood and also the removal of waste product between the embryo or fetus and placenta. UTERUS - The uterus or womb is the major female reproductive organ. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina; the other is connected on both sides to the uterine tubes. It is in the uterus that implantation of a fertilised ovum occurs and the embryo begins to grow.
VAGINA - The vagina, is the tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in women. The human vagina is an elastic muscular tube usually about 4 inches (100 mm) long and 1 inch (25 mm) in diameter (however, this can vary from woman to woman, just as penis size varies in men). It connects the vulva at the outside to the cervix of the uterus on the inside.
VAGINAL EXAMINATION – during an examination a midwife will insert two fingers into the vagina. This allows her to get information such as how dilated the cervix is, position of baby and whether membranes are still intact. VENTOUSE DELIVERY – the use of a suction cup to aid the delivery of an infant.
VULVA – This is the name given to the female external genital organs.
|